Anyone who wants to become an entrepreneur needs capital. Especially when buying a company, the capital requirement is much higher than when starting a new business.
It is therefore important to know what financing options are available. Moreover, it makes sense, to make the best possible use of its opportunitiesto obtain the most attractive conditions.
Don’t have much time to read? Our article at a glance:
- For company acquisitions and succession capital requirements and financing plan must be carefully thought through
- A meaningful Mix of equity, debt and funding programmes Ensures a stable financial basis
- The Financing discussions with the bank do not have to be unpleasantif you take our tips to heart
Table of contents
- Determine capital requirements
- Financing a company acquisition: basic financing structures
- The Vendor Loan / Vendor Loan
- Funding
- The forms of financing at a glance
- Example financing
- 11 tips for talking to a bank
- 1. basic principles: mapping collateral
- 2. complete documentation
- 3. financial statements
- 4. suitability and motivation of the buyer
- 5. business plan / business plan and forecasts after the takeover
- 6. present the financing concept
- 7. outline existing credits of the buyer
- 8. present repayment plan
- 9. describe the handover process / post-merger
- 10. further development of the company
- 11. involve M&A advice
- Conclusion
Determine capital requirements
With a Company takeover and the purchase in the context of a business succession, the capital requirement in connection with the purchase price is the most important milestone. Only when the capital requirement is known can one begin to make a to develop a corresponding financing concept and raise the necessary funds.
When determining the capital requirements, it is important to calculate in such a way that a future growth phase or investments after the takeover also reliably cover the liquidity requirements. In the worst case scenario, if the financing framework is too small, bank discussions will have to be held again just a few months after the takeover. Post-acquisition financing is not one of the easiest tasks for the financing partner and the entrepreneur. If, on the other hand, too much capital is raised for the business acquisition, unnecessary costs are incurred, e.g. in the form of interest.
In the case of a company acquisition, the immediate capital requirement is usually higher than in the case of a new start-up. Because a Company takeover or business succession is more expensive than starting a new business. Whereas with a new start-up the capital requirement is spread over a longer period of time, a business takeover or succession is much more capital intensive at the time of purchase. The buyer takes over a complete foundation, such as machinery, vehicle fleet, stocks and has running costs, such as salaries, rents, etc.
The biggest cost in taking over a company is, of course, the purchase price itself. In addition, the fixed assets (if unusually not included in the purchase price) can be added. Investments that may be necessary, e.g. for modernisation, must also be taken into account when determining the total capital requirements.
Added to this are the liquidity requirements for running costs and the procurement of possible use of goods.
Depending on the form of the company, the buyer should also take into account his private capital requirements. After all, living expenses and private obligations must also be met. As a rule, the entrepreneur (does not apply to corporations) withdraws a certain amount every month for private purposes. This money is then no longer available to the company and, in the event of a critical business development, strained liquidity can cause a bottleneck.
Business valuation
In order for the seller and buyer to agree on a purchase price, a company valuation makes sense. Often the two parties’ ideas about the value of the company naturally diverge.
For the seller, the company usually also has a high emotional value. The buyer lacks this and understandably does not want to pay for it.
An objective value can be determined through a company valuation. You can easily use a calculator on the Internet for a simple calculation (but this is then usually only the “thick thumb”) of the respective company.
However, it makes sense to carry out a detailed analysis and calculation of the company. This will The valuation is determined primarily with the capitalised earnings value method, according to the recognised standard IDWS1 or, in the case of craft enterprises, also according to the AWH method. In Austria, the valuation is based on the KFS/BW 1 expert opinion.
It is important to turn to an experienced management consultancy for a company valuation. They are familiar with the relevant procedures and can determine the company value professionally and transparently. A well-founded company valuation is also advantageous for taking out a loan with a bank or savings bank.
Use our company value assessment from more than 2,000 company valuations.
Financing a company acquisition: basic financing structures
Who has a Buy company not only needs to know how much capital it needs, but also how to raise it. There are several possibilities and different structures. In some cases, the transitions are fluid and the individual forms of financing cannot be clearly distinguished from one another. It is therefore all the more important to to think carefully in advance about how the capital for the company purchase is to be raised. Before you search through the flood of information on the internet, we will give you a comprehensive overview here.

Equity
In the case of a company acquisition approx. 10 to 30 percent equity capital (own funds/ collateral) should be available. This secures the basic financing with a bank and makes it easier to raise the remaining capital. Funding programmes often require a certain equity ratio. Banks and savings banks grant a loan more easily with a higher ratio (lower risk).
However, there are also financing partners who provide special forms of equity, which is usually more expensive than classic bank financing.
Equity capital
In this process, external investors provide money to the company. And they do so without the usual collateral. Long-term participation has a positive effect on the buyer’s credit rating. This strengthens the basis for negotiations with banks.
There are two types of shareholdings in a company: the dormant shareholding and the open shareholding.
Debt capital
Debt capital is always debt or liabilities. Debt capital can be raised from a wide variety of lenders in various forms.
Bank loan
Taking out a loan from the house bank is the classic case of a loan. In order to obtain a loan in the desired amount, thorough planning and a sound business plan are absolutely necessary. In addition, sufficient time must be planned, as the bank requires a certain processing time.
Investment credit
If the loan is primarily needed to finance certain investments after the company purchase, the buyer can take out an investment loan.
There are special commercial banks for this and also options of public funding. The amount of the loan should depend on the company’s earnings and be repayable in four to seven years.
Private loans
With private loans (e.g. in the family with parents or relatives and friends) everything is possible. There are no restrictions regarding the loan amount, term, interest, collateral and repayment. However, it is advisable to regulate all these framework conditions contractually. Credit agreements should always be in writing. This is how to avoid trouble in connection with the purchase of a company.
Private investors can be any person who is willing to invest in the company or in the future owner or shareholder.
Promotional loan
These are made possible by special Promotional banks of the federal states and KfW. The aim of these banks is to support start-ups and business successions.
They grant publicly subsidised and low-interest loans. A subsidised loan is available in many different variants. Often there are repayment-free years at the beginning of the loan term. Many promotional loans also offer a release from liability. This reduces the default risk for the bank. In addition, it may be willing to grant a loan if the collateral is insufficient.
Most promotional loans can be applied for via the house bank.
Mezzanine capital incl. example
The Mezzanine capital is a special form of financing. It represents a hybrid form of equity and debt capital.
Depending on the form it takes, banks value it as debt or equity capital. This increases the creditworthiness, as it increases the equity ratio.
There are different forms of mezzanine capital. The most common form is the silent partnership.
In the case of a silent partnership, a shareholder pays a contribution. However, he does not receive any shares in return. In return for his contribution, he receives a share in the profit or loss. However, the silent partner does not participate in the assets of the company.
It also does not appear externally, does not interfere in the management of the company and does not have any other rights of co-determination.
In our online seminar on company acquisitions, you will be comprehensively prepared for this complex topic.
Example:
Mr Müller would like to take over a company. This company succession costs 500,000 EUR. He himself has 25,000 EUR in own funds. This corresponds to an equity ratio of 5 percent. This is too little to apply for subsidies and a loan from his bank. He therefore looks for a silent partner.
This person contributes EUR 100,000 to the company. This money is considered equity, as the silent partner does not have a stake in the company and also has no rights or obligations. He only participates in the profit or loss of the company. The participation is subordinate.
Overall, Mr. Müller can therefore now show an equity ratio of 25 percent. This strengthens his creditworthiness enormously. This means that he has a good chance of closing the remaining financing gap with subsidies and a loan.

The Vendor Loan / Vendor Loan
With a Seller loan the loan comes directly from the seller of the company. He thus “defers” part of the purchase price to the buyer and acts as a bank himself.
This means that the buyer does not have to pay the entire purchase price when buying the company, but can pay part of it later or even in instalments. This means an enormous relief for the buyeras he can then use this money for other purposes.
The vendor loan is also a vote of confidence. It shows that the vendor believes in the continuation of the company. This also has a positive effect on the bank, where a further loan may have to be applied for.
A vendor loan can/must also be contractually structured as a subordinated loan. This means that the seller only gets his money back after all other creditors.
This is also positively assessed by a bank.
Funding
The federal government, the Länder, local authorities and also the EU offer numerous support programmes. Under certain conditions, they provide money for the purchase of companies. The aim is to promote the economy of regions and to secure or expand jobs.
Public funding must always be applied for before the takeover. This is not possible retroactively.
The following funding can be applied for:
KfW Bank: ERP capital for start-ups
- Various subordinated loans up to EUR 500,000 are offered
- Credit is attributed to equity
- Entrepreneurs do not have to provide collateral
- Personal liability is required
- There must be 15 per cent equity capital
- Together with the equity capital, up to 45 percent of the purchase price can be financed
Public development banks
- z. E.g. guarantee banks
- Loan and equity financing
- Issuance of state guarantees for submission to the house bank
- Equity ratio is increased
The forms of financing at a glance
The acquisition of a company requires a large amount of capital. In the rarest cases, this is available in own funds. But there are many possibilities. Both the house bank and business partners, family, private investors and the state can provide funds. Even the seller of the company is eligible as a lender.
Depending on the financier, there are many different forms of financing. A financing mix of different forms is usually the best option.
Example financing
As already described, Mr. Müller would like a Buy a company with a capital requirement of EUR 500,000. He brings EUR 25,000 in equity capital. A silent partner contributes EUR 100,000 to the company.
Next, Mr Müller applies for funding. He receives another EUR 200,000 via KfW Bank. He does not need any collateral for this and this money is also added to the equity capital.
Now he needs another EUR 175,000. He gets this loan from his house bank at the desired conditions without further searching, since he can demonstrate good solvency through previous fundraising.

11 tips for talking to a bank
If you want to take out a loan from the bank to buy a company, you have to be well prepared. The bank must be convinced. Because the bank calculates its default risk. The higher this is, the more expensive the loan will be in terms of costs and repayment.
1. basic principles: mapping collateral
In order to improve your personal creditworthiness, you can provide the bank with collateral. These can consist, for example, of mortgages on real property. Other forms of collateral include claims against third parties, other tangible assets, cash reserves and securities.
If you no longer have any collateral of your own, you can also appoint guarantors. These can be business partners or friends and family in particular. In the event of an emergency, they will stand in for the liabilities.
2. complete documentation
A loan application to the bank should be well prepared. The more documents about the company are provided to the bank, the better. The documents should be well and thoughtfully prepared and, above all, transparent.
The bank wants to get an accurate insight into the company. Both into the past and into the future in the form of forecasts. This has a considerable influence on the granting of loans.
In order to be optimally prepared, it is advisable to ask before the bank interview which documents are absolutely necessary.
However, the following documents are relevant in any case:
Description of the investment project
This description must contain all important data about the company. In addition, the advantages of the company should be described in detail. But also the investment calculation and the realisation period, the required loan amount and the repayment modalities should not be missing from this description.
Annual financial statements with balance sheet or income statement
With the information on the earnings and financial situation, important key figures can be calculated. These include, for example the company’s return on sales, return on equity and cash flow.
These ratios are an important reference point for the bank. It makes sense to submit these documents with an audit certificate from the tax advisor.
Current business management analysis (BWA)
This shows the composition and development of income and expenses. The bank is thus comprehensively informed about the course of the current business year.
The BWA also includes a list of totals and balances as well as information on depreciation, changes in inventories.
Turnover and profit plan with explanatory notes
The possible development of a company is one of the most important aspects for the bank. Here, the possible turnover as a result of detailed sales planning must be compared to the necessary expenses.
Liquidity plan with explanations
The liquidity plan shows the monthly income and expenditure. The liquidity plan should be drawn up for the current and coming business year of the company. Payment dates and due dates should also be listed. In this way, the monthly surplus or deficit can be calculated and, if necessary, clarified with the bank.
List of payables and receivables
This list plays an important role for the bank when granting a loan. It uses it to assess the solvency of a corporate loan. In the case of receivables (debtors), it assesses the solvency of the debtors.
3. financial statements
In order to give the bank a comprehensive insight into the company, the balance sheets and interim balance sheets of the last 3 years should be available. The results of the current year should also be available at the bank meeting.
4. suitability and motivation of the buyer
The bank attaches importance to the suitability of the buyer. For this purpose, a distinction is made between two factors. Both professional and commercial suitability count. These points are easy to check. Something The motivation of the buyer in the purchase of a company is more difficult. However, this should be present to the extent that the buyer also receives the acceptance of the employees. Only in this way is it possible to continue the company successfully.
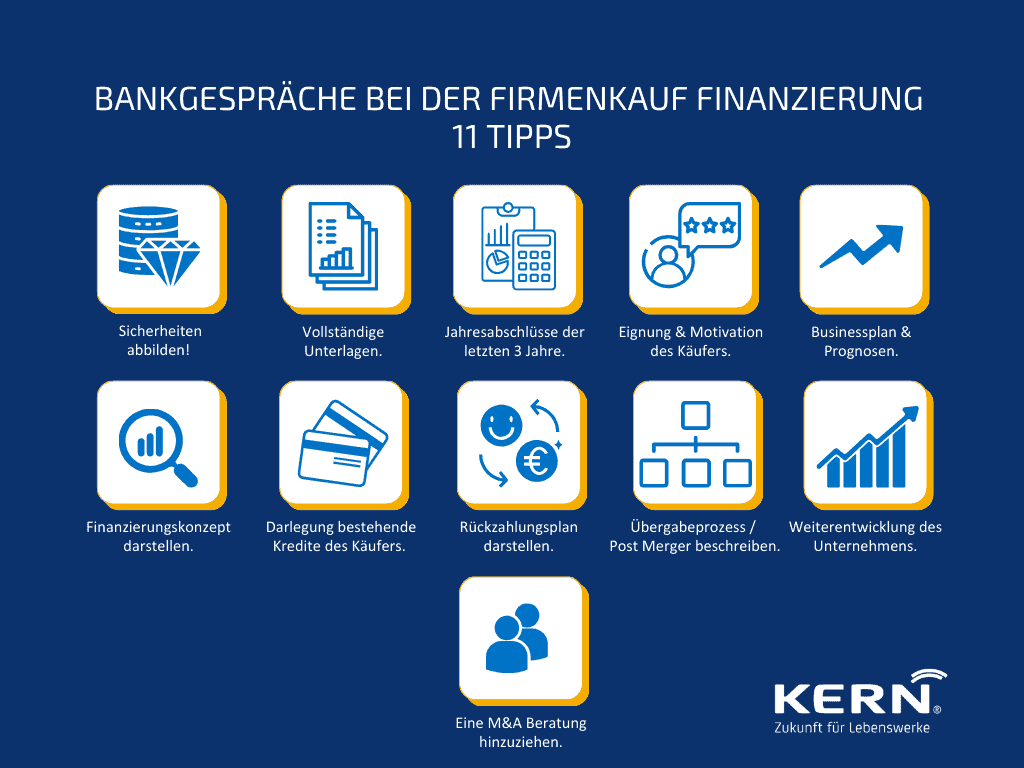
5. business plan / business plan and forecasts after the takeover
The buyer’s own business plan is also important. The buyer should formulate in his own words what plans he has after buying the company and how he intends to implement them. This should also include forecasts of how the new entrepreneur sees his success and the further development of the company.
6. present the financing concept
The bank is not only interested in its own credit. For them, extensive information is important. The buyer should therefore present a coherent financing concept. This should include the Company valuation, the purchase price and the corresponding financings be listed for the acquisition of the company.
7. outline existing credits of the buyer
To give the bank a comprehensive insight, all current loan agreements should be listed. The information required includes the amount of the loan, the repayment, remaining term and the collateral.
8. present repayment plan
For the bank, the repayment rate in combination is an important point. The buyer should therefore consider in advance how high the loan should be, what the monthly repayment can be and what term he needs. The more coherent and realistic the repayment plan is, the more likely the bank will approve the desired loan. However, it is also important that the term is not too long. A shorter term is always useful to convince the bank.
9. describe the handover process / post-merger
The bank naturally wants to know exactly how the transfer of the business, or more precisely the Post Merger Integration (PMI), is planned. Because in order to be able to successfully continue a company, this is an essential point. After all, the buyer must be introduced precisely to the company structures in order to gain a comprehensive insight into the company. The acceptance of the employees also depends on how the handover of the company is planned. It is therefore advisable to submit a precise concept to the bank.
10. further development of the company
The bank is also interested in the ACTUAL state of the company. But further development after the company has been acquired is also important. The buyer should therefore think in detail about the changes he wants to make in order to push ahead with further development. In this context, further forecasts are useful. The more detailed and thoughtful the information, the more likely it is that the bank will be convinced.
11. involve M&A advice
In order to be as well prepared as possible and to be able to present well-founded documents, it makes sense to make a M&A consulting for the entire company takeover. M&A consultancies usually have many years of experience and know exactly which documents need to be required and prepared. Also with the Calculation of key figures, preparation of forecasts, etc. supports M&A consulting.
Would you like to buy a company or acquire a shareholding? We have the right offers.
Conclusion
There are a variety of financing options for buying a company. A wide variety of financing mixes are possible. However, the order in which the loan is drawn down is important, because it affects the next step. Outside capital in the form of a loan from the house bank is usually necessary. However, this should be the last step to be taken.